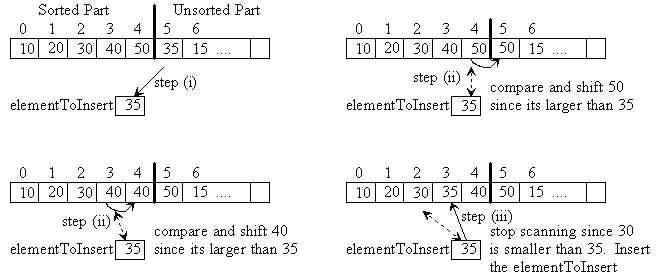
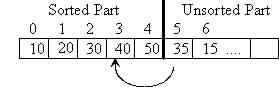
The Insertion sort is another sorting algorithm where each iteration of the "main" loop extends the size of the sorted part by one element. The idea is to extend the sorted part by inserting the first unsorted element into the correct spot in the sorted part. In the below example, 35 should be inserted between 30 and 40 in the sorted part. To do this, you must find the correct spot to insert 35 and shift larger elements (40 and 50) to the right one location to make room for 35. The following algorithm calls a subprogram Insert which combines finding the insertion spot and shifting larger elements as follows:
i) Copy the first unsorted element into a temporary variable named "elementToInsert"
ii) Scan the sorted part of the array from right-to-left. As you scan, shift larger sorted elements to the right one location to make room for the elementToInsert. Stop scanning when you reach the front of the array or you encounter a sorted element that is less-than-or-equal-to the elementToInsert.
iii) Insert the elementToInsert into the array
The following example show these steps:
|
Reg. # |
APCS Name |
APCS Role |
|
|
R0 |
a1 |
Argument 1/integer result/scratch reg |
Caller-saved registers - subprogram can use them as scratch registers, but it must also save any needed values before calling another subprogram. |
|
R1 |
a2 |
Argument 2/scratch register |
|
|
R2 |
a3 |
Argument 3/scratch register |
|
|
R3 |
a4 |
Argument 4/scratch register |
|
|
R4 |
v1 |
Register variable 1 |
Callee-saved registers - subprogram must save them if it wishes to use these registers, but it can rely on an subprogram it calls not to change them. |
|
R5 |
v2 |
Register variable 2 |
|
|
R6 |
v3 |
Register variable 3 |
|
|
R7 |
v4 |
Register variable 4 |
|
|
R8 |
v5 |
Register variable 5 |
|
|
R9 |
v6/sb |
Register variable 6 |
Used for reentrant code |
|
R10 |
v7/sl |
Register variable 7 |
Stack limit register used to check for stack overflow |
|
R11 |
fp |
Frame pointer |
|
|
R12 |
ip |
Scratch register / new static base in inter-link-unit calls |
|
|
R13 |
sp |
stack pointer |
Points to "top" of current call-frame |
|
R14 |
lr |
link register/scratch register |
Receives return addr. on BL |
|
R15 |
pc |
program counter |
Points to next instruction to execute |
Implement the following two Insertion sort subprograms (i.e., InsertionSort and Insert) using the ARM APCS calling convensions. Include all assembly language directives (EXTERN, AREA, EXPORT, END, etc.) to make each a complete subprogram. For each subprogram, include comments indicating what argument or local variable each register is holding.
(Note: "length" argument to InsertionSort is a count of elements in the array "numbers")
InsertionSort(numbers - address to integer array, length - integer)
integer firstUnsortedIndex
for firstUnsortedIndex = 1 to (length-1) do
Insert(numbers, numbers[firstUnsortedIndex], firstUnsortedIndex-1);
end for
end InsertionSort
Insert(numbers - address to integer array, elementToInsert - integer, firstSortedIndex - integer) {
integer testIndex;
testIndex = firstSortedIndex;
while (testIndex >=0) AND (numbers[testIndex] > elementToInsert ) do
numbers[ testIndex + 1 ] = numbers[ testIndex ];
testIndex = testIndex - 1;
end while
numbers[ testIndex + 1 ] = elementToInsert;
end Insert
You are encouraged to work in small groups (2-4) on this pencil-and-paper exercise. Each group should turn in ONE copy of their answer to my mailbox in the CS office (Wright 219).
List all the names of students in your group: ____________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
Start your code on this page and include additional sheets of paper as necessary. There is a stapler in the CS office (Wright 219).