Test Two Study Guide - FALL 2014 - Friday, December 5th
i. Peter Venkman - Understand the problem. Focus on WHAT.
(a) What is given? What is known?
(b) What is the goal? What is the unknown?
ii. Raymond Stantz - Develop a PLAN. Focus on HOW to solve it.
How to get from (a) to (b).
HOW to use the known givens to get to unknown goal
or result.
What formulas, such as SOH, CAH, TOA involve
the (a) known and the (b) unknown aspects?
iii. Egon Spengler - Implement and carry out your plan using the
tools such as NetLOGO, Data Flyer, After Effects,
Maya, Windows calculator, and hand calculations
with pen and pencil to carry out and clearly
SHOW your WORK step by step!
b
Do you understand the a = --- (d) formula and concepts.
c
Can you look at a Monte Carlo problem
and find the a,
the b, b
the c, The -----
the d? c
and figure out which of the four parts is the goal, the unknown?
It is all in the above study guide PDF. See page CCC. See CCC.
BICTION = if the INK don' flow, the understanding don't grow.
Take some notes, use some lead or ink, consume some scratch paper.
Practice. Don't just read over and look at. DO! Nike. Just DO it.
Worksheet - Oct 21st midterm followup exercise 8 questions.
Find the best fitting (smallest "Sum of squares of deviations:")
line
f(x) = mx + b
for the following two points using Data Flyer:
-5 -1 <------ point a
0 3 <------ point b
Now, REFRESH the Data Flyer application and try these three points:
-5 -1 point a (same as before)
0 3 point b (same as before)
-2.5 2 point c <----- ths new 3rd point
Can you get the Sum of squares of deviations: 0.67 or less????
Note: It is helpful to click on "Light Grid Lines"
When you get the 0.67 or less
for the Sum of the squares of the deviations,
after doing enough Change Function and Slider adjusting,
you have discovered your
best fitting function
f(x) = mx + b, or
y = mx + b What is m? What is b?
Know the idea
of the RISE
(the y2 - y1 or y difference
or distance or change)
and
the RUN
(the x difference, x2 - x2,
the x distance or change)
E E R
S S I
I I S
R or R E
R U N R U N R U N
Run across (the x-axis) Rise UP (on the y-axis)
Rise
------ = slope of the line connecting the two points
Run
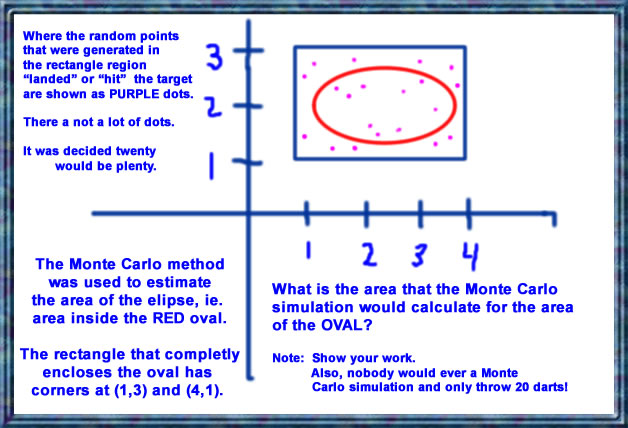
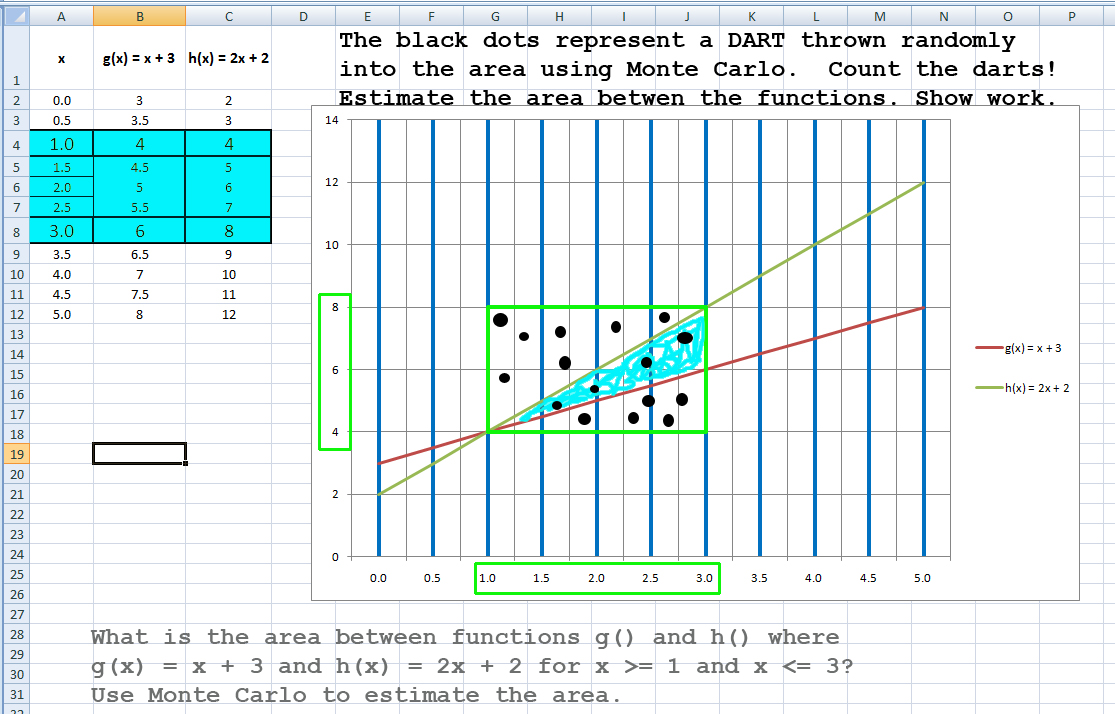
Netlogo TURTLES randomly scatter, then turn into either a COW or a HOUSE depending on whether they hit the BULLS EYE or missed the oval shaped bulls eye.
Know and understand the formula for coming up with a Monte Carlo estimated area when you know the proportion of or the actual count of "darts" that landed inside the area of interest.

Example: Look at the following diagram which shows a solid point for every dart that was thrown
and where it hit inside the target area. The target area is the rectangle there you see
that goes from x = 1 to x = 3 and from y = 4 to y = 8.
(Note: for practical purposes, only 16 or 20 darts were thrown
in the examples shown here).
Calculate what the estimated area of the region above function g
and below function h would be? (The area BETWEEN function g and function h).
Please show your work and calculations.
I need to see your process of arriving at the result.
You will get partial credit if your equation is correct, but you just had a simple calculation, arithmetic error.
You will NOT get full credit for just having the correct answer, so show the process for that reason too.